
SSL HANDSHAKE EXCEPTION
Almost every app nowadays requires to be connected to an API service. This involves setting up the app to be calling the API services and fetching the data properly and handling errors and exceptions. If you have worked on any such applications, there is a high chance that you have encountered this particular exception named SSL HANDSHAKE
WHAT IS SSL HANDSHAKE EXCEPTION
We know that calling an API service requires the backend database to be included in a server, which is hosted and connected to a domain. Such domain connection is made secure by adding an SSL certificate.
This SSL certificate makes the connection secure and encrypted sensitive information. The SSL certificate is not required to be a single certificate, but can be a chain of certificates interlinked to each other. There are two types of Certificate Authorities, called route CA and intermediate CA. We can add multiple intermediate CAs to our SSL as per our requirement. You can refer more about this here.
ROLE OF SSL IN ANDROID APP
When an Android app tries to access the server via api, it first checks whether the server is secure, and then validates whether the intermediate CAs added to the SSL is one among the accepted certificates of Android. To find the list of certificates that are accepted as valid in your device, go to Settings → Privacy → Encryption & Credentials → Trusted Credentials.
If your server SSL doesn’t have any of the accepted certificates as an Intermediate CA, then the app will throw an SSL Handshake exception, stating that the connection is not secure. The same will happen, if you try to fetch data from a non-secure connection. This can be easily resolved by letting the app to ignore whether the connection is secure or not and go-ahead to fetch data.
But, by doing this, the app becomes easily vulnerable for Man in the Middle attack.
MAN IN THE MIDDLE ATTACK
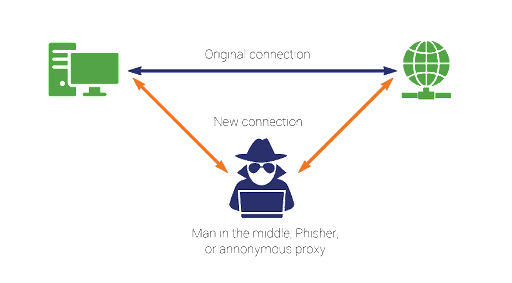
A man in the middle (MITM) attack is a general term for when a perpetrator positions himself in a conversation between a user and an application. To explain this in practical terms, we can take an example of an ecommerce application. Consider, the user adds a few items in the cart, and proceeds to pay for the items. Ideally, we fire an api, to pass the amount to the payment gateway. By using the MITM attack, the perpetrator can read the api along with the parameters, and later fire the api, with modified params so as they can pay whatever they want for all the products. This is a serious issue for applications which involve sensitive user information too.
HOW TO PREVENT FROM MITM ATTACK
The very first thing that needs to be made sure is that the app does not use a trust manager to trust all certificates as valid. If you are using Retrofit for API calls, make sure that the HTTP client you are adding is the basic OkHttp client, but not the modified client with trustmanager implemented.
After that, make sure the server which you are connecting to is secure. To put it in simple terms, the endpoint should be https and not http. But this is not enough to say, the connection is secure. Even though the website has an SSL certificate added to it, it doesn’t mean it has included the necessary intermediate certificate which is required by android. So how to test the same? You can use the following terminal command to check whether the domain you are accessing has all the necessary certificates.
openssl s_client -connect www.gmail.com:443
You can replace “www.gmail.com” with your own domain. Once you run this command in your terminal, you will receive a chunk of details about the domain. The thing you need to look into is the initial part, which gives out the details about the intermediate certificates that are added.
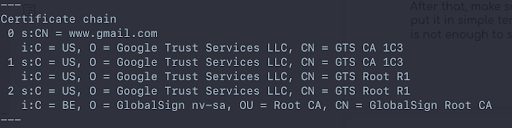
If you notice, gmail.com has added GlobalSign as one of the intermediate certificates. If you go to the Trusted Credentials Screen in your android phone, you’ll see that it accepts GlobalSign as a valid certificate.
In your domain, if none of the certificates which are added to the SSL, is supported by Android, then you need to speak with the SSL provider regarding this and request for the approved certificate to be added and chained in properly.
With these verification, we are half-way in making our app more secure from any phisher attack. But how do we make it even more secure? Let’s look at this further.
CERTIFICATE PINNING
To put it in simple terms, Certificate Pinning is the process of letting the Client know which are the valid certificates to be trusted and permitting the network calls, only if those certificates are present. This acts as an additional layer of security so that in case the attacker presents a duplicate certificate which might seem legit, and thus be able to decrypt the data between the server and client.
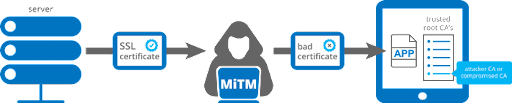
There are many ways with which you can implement this particular certificate pinning. But the most recent way and the most optimal way to implement this is by using Network Security Configuration (NSC). The only downside of using this is that it is available only for api level 24 and above.
To implement this, create a network_security_config.xml in res/xml/network_security_config.xml
Make sure to mention in the manifest that you have added a Network Security Config file.
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?>
<manifest
xmlns:android=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
package=“co.test.yourApp”>
<application
android:networkSecurityConfig=“@xml/network_security_config”>
…
</application>
</manifest
With that done, all that is left is to add the proper data to the networkSecurityConfig file. One can do that manually, but there is a tool available online that we can utilize to auto-generate the config file for us.
Visit Approov Static Pinning to see the following options displayed. Select the config tab, and enter your domain name to which the app is connected to via API.
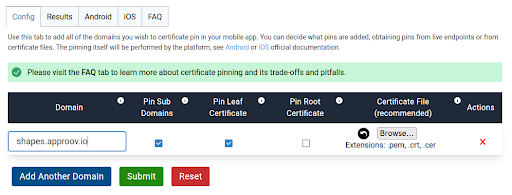
Click on Submit or add further domains, if you access multiple domains. Once the process is done, go to the Results tab to check everything is fine with the certificate generation.
Now click on the Android tab, and you can see an xml file which was generated.
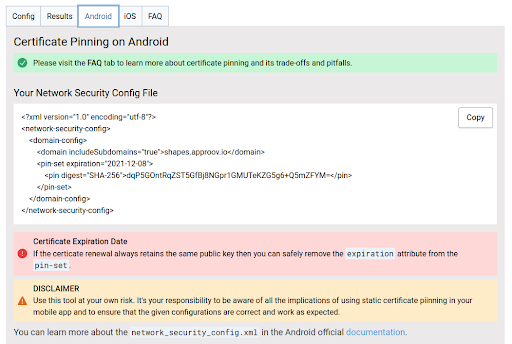
Make sure it has the proper domain name, expiry date and the sha-256 fingerprint. These are very essential for the android sdk to consider it as a proper Network Security Config file.
Once the validation is done, copy the content to your previously created config file in your source code and replace the same. If you have followed everything properly your app is now configured for certificate pinning which helps us to avoid Man in the Middle attack and other such middleman proxy attack techniques.
To simulate the proxy attack, you can utilize the postman to create a proxy connection with the target android device and check whether the app allows api calls when the proxy is ON. You can refer to this article to learn how to set up the proxy attack using postman.
Apart from this, if you want to learn about the security principles and methods to implement to avoid this, you can refer to the following articles.


 +91-984-5825982 | +91-996-4689921
+91-984-5825982 | +91-996-4689921 sales@cumulations.com
sales@cumulations.com Send your requirement
Send your requirement 