
Flutter Flavors
When developing apps, it is very important to separate out development and production environments. Flavors allows us to create multiple versions or variants of our app with the same codebase making it easy to create and test features without the risk of destroying the production data. Let’s look into more information about how developers from App Development Company in Bangalore enable flutter flavours in their codebase.
When to use Flavors
- Suppose you have a paid and a free version of the app, you can limit the features in the free app and expose all the other features in a paid version for the app
- When you wish to address the issue of having a separate project code for each version of the app while still having one project code.
- A scenario in which the admin user app should have all the functionalities as that of the customer app. But in addition, admin users need to have access to the statistics page and be able to see the app with different colors and resources while making sure that your admin app’s analytics are not mixed with its custom app.
Advantages of Flavors
- They make the code much easier and faster to navigate through as everything related to the specific product flavor would be kept in their corresponding folders.
- They address the issue of having a separate project code base for each version of the app.
Android Product Flavors
With regards to android, the product flavors are defined in the app gradle module.
Go to build.gradle file inside <app dir>/android/app/ director and add the following configuration shown in the below image.
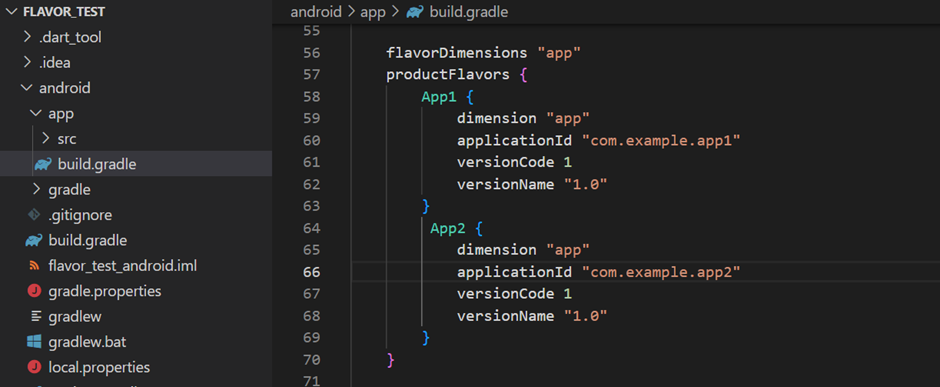
To have different App Names for different flavors, in <app dir>/android/app/src/main/ change from android:label=”your App Name” to android:label=”@string/app_name”
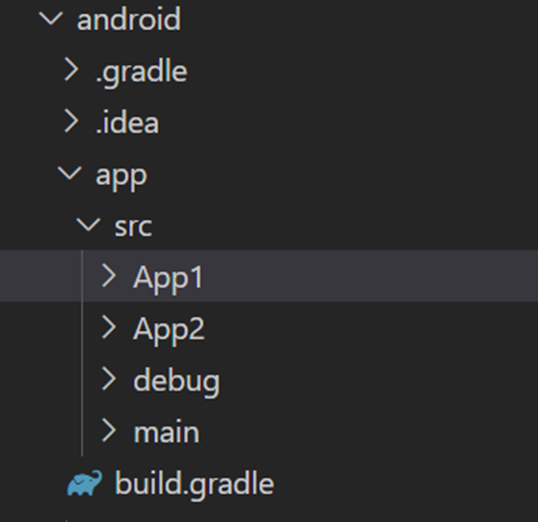
Create App1 and App2 folders in <app dir>/android/app/src/, use the below image for reference.
In the new folders App1 and App2 create folder named res and within it the
folder named values. In the values folder create a file called strings.xml with the contents as below.
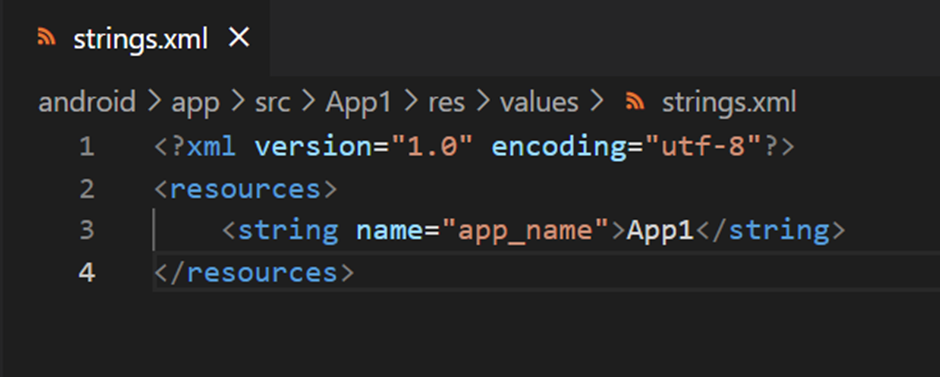
The App1 in the string tag is the app name of the first flavor. And similarly in the Android Manifest.xml add the following line inside the application tag.
android:label=”@string/app_name”
iOS Schema
Create a configuration file in the ios/Flutter folder for every flavor, including the Generated.xcconfig file, setting FLUTTER_TARGET to the main file required by the target and the bundle_suffix. Include the generated Pods xcconfig file as well (as Flutter does in the predefined Debug.xcconfig and Release.xcconfig
Then create a new scheme for every flavor. Also check the shared checkbox in the dialog.
Now select the Runner project and add the configurations you need selecting as configuration file the one created before. You need to have two configurations for each flavor named with Release-[flavorName] and Debug-[flavorName]. Names are really important for flutter matching reasons.
In order to use the right configuration when archiving the iOS app, you need to edit each scheme, setting the archive build configuration to the one you need. Regarding the icons, they can be set in the Runner target in the Asset Catalog App Icon Set Name option.
App setup
The first thing to do is to split the main entry point of the app. Then, we create a configuration class that can be changed depending on the flavor of the app. With this setup, the content of the app should never have to change.
Each main file will have to initialize its own configuration and pass it to the common main file. The common main file will then launch the Flutter app along with the configuration.
I. Different Main Files
We will have two main files for two apps. Let’s name them main_app1.dart and main_app2.dart. It is important that there is one main() function in each file. In the picture below
main_common.dart contains common code for our app such as for initializing some variables.
main_app1.dart contains code specific to App1.
main_app2.dart contains code specific to App2.
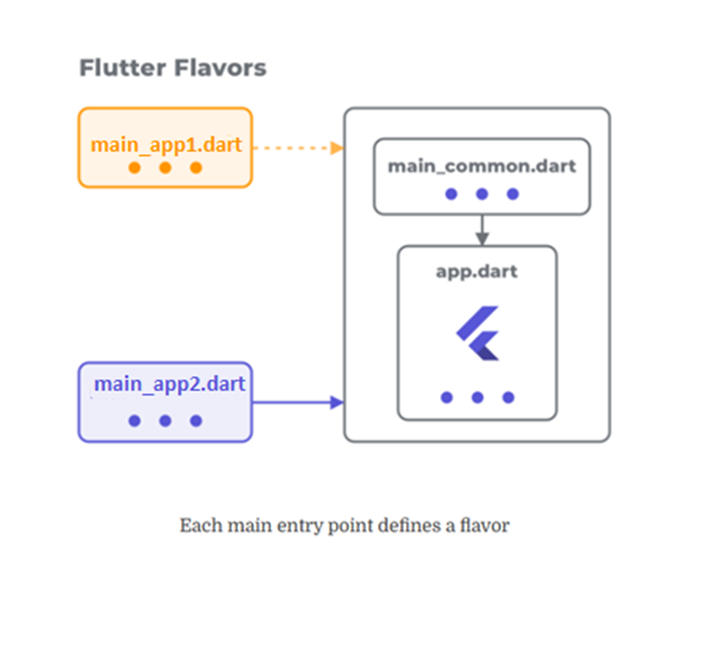
Each file main_app1 and main_app2 will call the primary main_common.dart. Then, the specific configuration class will be used as a parameter to call the primary main. The main_common.dart is the one that will launch the app.
II. Configuration Class
This will be the class that contains the different dependencies that we want to use according to flavor.
Here, the configs have their own titles and repositories and theme colors. We use an AppConfig interface so that each implementation will follow this interface. The main app only uses the interface and does not need to know what type of AppConfig it is.
A better approach to pass this config around is to use dependency injection libraries such as Provider and Flutter BLoC. With these libraries, we can easily access and use our config class across the app.
Running the App in Different Flavors
The only thing we need to do is to run flutter with a target parameter specifying our flavored main file.
At the root of your project directory:
flutter run -t lib/main_App1.dart
flutter run -t lib/main_App2.dart
Running from Visual Studio Code
If you want to run the app directly from VS Code, update the launch.json file found under the .vscode directory. You can also update the file by doing Run > Add Configuration.
Each configuration inside this file contains a field called program. This field points to where flutter will run the main file. We just need to add our own configurations.
Splitting your app using flavors and configurations is a cleaner way to speed up our development process.
FAQ:
Q1: What are Flutter Flavors and why are they important?
A1: Flutter Flavors are a powerful feature in Flutter that allows you to create multiple versions or variants of your app using the same codebase. This separation of flavors in Flutter is crucial for developing different app versions, such as free and paid versions, or distinguishing between admin and customer functionalities. Using Flutter Flavors helps in maintaining and testing features without risking production data.
Q2: How do Flutter Flavors benefit app development?
A2: Flutter Flavors offer several advantages:
– Flutter Flavors make the codebase easier to navigate by organizing flavor-specific code into separate folders.
– They eliminate the need for separate project codebases for different app versions, streamlining development and maintenance.
Q3: How can I set up iOS build variants for different app flavors?
A3: To set up iOS build variants:
- Create configuration files in the `ios/Flutter` directory for each flavor. These include the `Generated.xcconfig` file with settings like `FLUTTER_TARGET` and `bundle_suffix`.
- Define schemes for each flavor and select the shared checkbox.
- Add configurations in the Runner project, ensuring you have configurations named `Release-[flavorName]` and `Debug-[flavorName]`.
- Adjust scheme settings to use the appropriate configuration when archiving the iOS app.
Q4: What role do Flutter Strings XML and flutter strings.xml play in setting up flavors?
A4: Flutter Strings XML and flutter strings.xml are used to define flavor-specific resources, such as app names. For Android, you need to:
- Update the `build.gradle` file to include different product flavors.
- Create folders like `App1` and `App2` in the `src` directory.
- In each folder, create a `res/values/strings.xml` file to define flavor-specific strings like app names.
Q5: How do you manage configuration across different Flutter Flavors?
A5: Manage configurations by:
- Creating separate main entry point files, such as `main_app1.dart` and `main_app2.dart`.
- Implementing a configuration class that defines dependencies and settings for each flavor.
- Using dependency injection libraries like Provider or Flutter BLoC to access configuration throughout the app.
Q6: How can I run my app in different Flutter Flavors from the command line?
A6: Use the `flutter run` command with the `-t` option to specify the main file for each flavor. For example:
- `flutter run -t lib/main_App1.dart`- `flutter run -t lib/main_App2.dart`Q7: How do I configure flutter strings.xml and other settings in Visual Studio Code?
A7: Update the `launch.json` file in the `.vscode` directory to include configurations for different flavors. Each configuration should specify the correct main file using the `program` field. Add new configurations by navigating to Run > Add Configuration in VS Code.
Q8: Why is it important to use flavors in Flutter?
A8: Using flavors in Flutter helps in managing multiple versions of the app efficiently, avoiding code duplication, and ensuring that each version has the appropriate features and settings. It streamlines the development process and improves the overall maintenance of the application.
Author: Cumulations Technologies Pvt Ltd a Flutter App Development Company in India.


 +91-984-5825982 | +91-996-4689921
+91-984-5825982 | +91-996-4689921 sales@cumulations.com
sales@cumulations.com Send your requirement
Send your requirement 